Mental health is a cornerstone of overall well-being, yet it often remains a topic of misconception, stigma, and neglect. It involves emotional, psychological, and social well-being, affecting how people think, feel, and act. From daily functioning to coping with stress, It influences nearly every aspect of our lives. Despite its critical importance, It has often been overshadowed by physical health, with many people struggling silently. This article aims to provide a thorough understanding of this problem , examine the challenges it presents, and discuss solutions and approaches that can help improve mental well-being for individuals and society as a whole.

Table of Contents
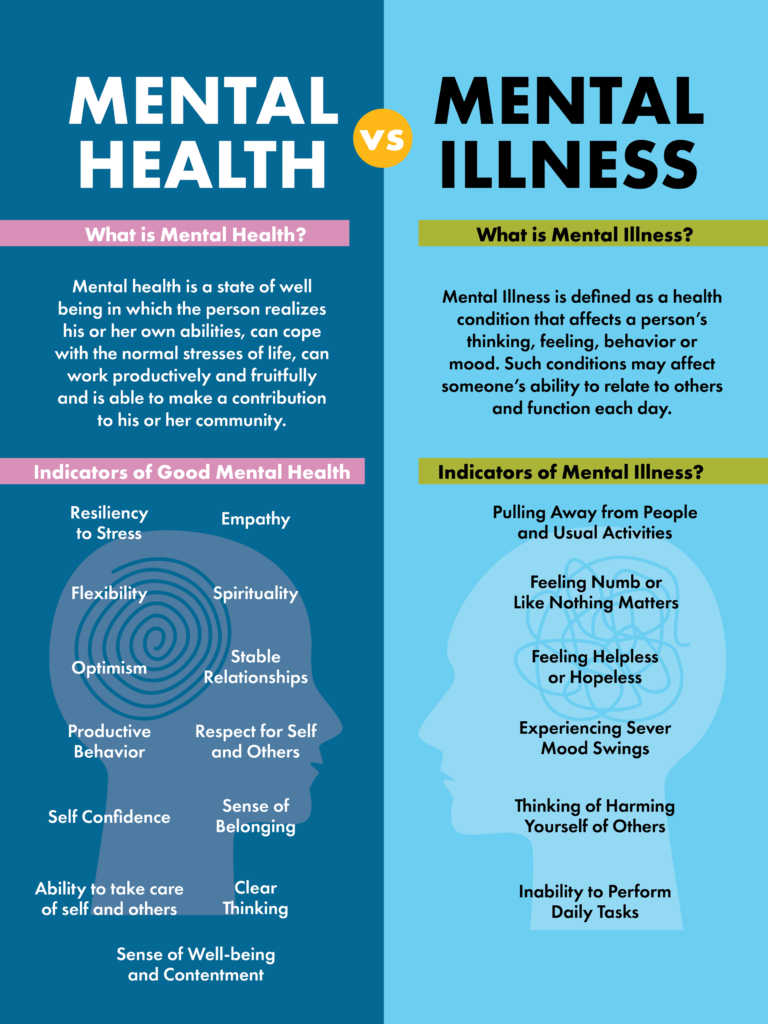
What is Mental Health?
It encompasses emotional, psychological, and social aspects of a person’s overall well-being. It affects how people think, feel, and act in daily life. It also determines how individuals handle stress, relate to others, and make choices. Positive mental health allows individuals to lead a fulfilling life, cope with stress effectively, build strong relationships, and contribute meaningfully to society.
The Importance of Mental Health
It is essential at every stage of life, from childhood and adolescence through adulthood. It affects how we think, feel, and behave, as well as how we relate to others. Healthy mental functioning helps individuals achieve personal goals, form stable relationships, and perform effectively in social and professional contexts. It also plays a key role in preventing mental illnesses and improving resilience.
One in four people will experience some form of mental health issue in their lifetime. It challenges can range from common conditions like stress, anxiety, and depression to more serious disorders such as bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and personality disorders. When left untreated, these conditions can have profound effects on an individual’s quality of life, leading to social, emotional, and even physical consequences.
Common Mental Health Conditions
- Anxiety Disorders: Anxiety is a normal human emotion, but when it becomes overwhelming or persistent, it can interfere with daily life. Anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. People with anxiety disorders may experience excessive worry, nervousness, or fear that disrupts their daily activities.
- Depression: Depression is more than just feeling sad or down. It is a persistent feeling of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities once enjoyed. It can affect sleep, appetite, and energy levels, and may lead to difficulty concentrating. Major depressive disorder is a severe form of depression that can significantly impact one’s ability to function at work, school, or in social relationships.
- Bipolar Disorder: Bipolar disorder is characterized by extreme mood swings that include emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression). These mood changes can impact behavior, sleep patterns, and judgment. The severity of the disorder varies, with some individuals experiencing only mild mood swings while others face extreme shifts that affect their daily functioning.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): PTSD develops after an individual experiences or witnesses a traumatic event. People with PTSD may relive the trauma through flashbacks or nightmares and may feel emotionally numb or detached from others. Symptoms of PTSD can significantly impact an individual’s relationships and ability to function normally in daily life.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): OCD is characterized by persistent, intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions). Individuals with OCD may engage in rituals or routines to alleviate the distress caused by these thoughts, even though the behaviors often provide only temporary relief.
- Eating Disorders: Conditions like anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder involve unhealthy relationships with food, body image, and self-esteem. These disorders can lead to severe physical and psychological consequences and often require professional treatment to address both the mental and physical aspects of the condition.
- Schizophrenia: Schizophrenia is a chronic mental illness that affects a person’s perception of reality, thinking, and behavior. Individuals with schizophrenia may experience hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, and difficulty distinguishing between what is real and what is not. Schizophrenia often requires long-term treatment, including medication and psychotherapy.
The Stigma Surrounding Mental Health
Despite growing awareness of mental health, stigma remains a significant barrier to seeking help. Many people with this conditions face judgment, discrimination, and social exclusion. The stigma surrounding mental illness can manifest in various ways, from negative stereotypes to avoidance or rejection by friends, family, and colleagues.
The fear of being labeled as “weak” or “crazy” may prevent individuals from reaching out for support or receiving proper treatment. This stigma can be particularly damaging in certain cultural contexts, It is not openly discussed, and those who seek help may be seen as a burden to their families or communities.
However, efforts are being made worldwide to reduce the stigma associated with mental health. Advocacy campaigns, education, and high-profile public figures speaking out about their mental health struggles have helped raise awareness and promote a more compassionate and accepting attitude toward those with mental health conditions.
The Causes of Mental Health Issues
The problems can arise from a complex interplay of genetic, biological, environmental, and psychological factors. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to mental health conditions, while others may develop them as a result of external stressors, traumatic experiences, or lifestyle factors.
- Genetic Factors: Its disorders tend to run in families, suggesting a genetic component to many conditions. However, genetics alone does not determine whether a person will develop a this type of disorder. It is thought to interact with environmental and psychological factors to influence risk.
- Biological Factors: Imbalances in brain chemistry or structural changes in the brain may contribute to the development of its conditions. Neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine play a role in mood regulation, and disruptions in these systems can be linked to conditions like depression and anxiety.
- Environmental Factors: Stressful life events, such as the loss of a loved one, financial struggles, or relationship breakdowns, can trigger or exacerbate mental issues. Living in poverty, experiencing abuse or neglect, and exposure to violence or discrimination can also increase the risk of developing mental disorders.
- Psychological Factors: Traumatic experiences, such as childhood abuse or witnessing violence, can have long-lasting effects on mental health. Additionally, individuals with certain personality traits, such as perfectionism or low self-esteem, may be more vulnerable to mental issues.
- Social and Cultural Influences: Social isolation, lack of support, and cultural attitudes toward this can affect an individual’s mental well-being. For example, in some cultures, The problems are seen as a sign of weakness, which may prevent people from seeking help.
Coping with Mental Health Challenges
The issues can be overwhelming, it is important to remember that recovery is possible. With the right treatment and support, many individuals can manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. There are several strategies for coping with mental challenges:
- Seeking Professional Help: Its professionals, such as therapists, counselors, and psychiatrists, are trained to help individuals cope with mental conditions. Therapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), psychotherapy, and medication, can be effective in treating a wide range of mental disorders.
- Building a Support System: Strong relationships with family, friends, and community members are crucial for emotional well-being. Support from loved ones can provide comfort and reassurance, and help individuals feel less isolated.
- Self-Care Practices: Regular physical activity, a healthy diet, and good sleep hygiene can have a significant impact on it. Mindfulness practices such as meditation, deep breathing, and journaling can help reduce stress and improve emotional regulation.
- Setting Realistic Goals: Establishing achievable goals can provide a sense of purpose and accomplishment, which can help improve self-esteem and reduce feelings of hopelessness.
- Avoiding Substance Abuse: Substance abuse, including alcohol and drugs, can exacerbate mental problems. Avoiding or addressing substance misuse is an important aspect of managing mental health.

Mental Health in the Workplace
It is increasingly being recognized as an important factor in workplace productivity and employee well-being. The demands of modern work life, including long hours, high stress, and lack of work-life balance, can contribute to mental challenges. Companies that prioritize employee mental health create a more supportive and inclusive work environment.
Employee assistance programs (EAPs), mental health days, stress management workshops, and open communication about mental health can help employees cope with work-related stress. Employers who acknowledge the impact of mental health on their workforce and provide resources for support can foster a healthier, more productive workplace.
Mental Health and Society
Society as a whole must take responsibility for promoting mental health awareness and providing resources for those in need. Governments, non-profit organizations, schools, and healthcare providers all play a role in ensuring that mental health services are accessible and effective.
Its education is key in schools, workplaces, and communities. By teaching individuals to recognize the signs and symptoms of mental health issues, society can reduce the stigma and encourage early intervention.
Additionally, greater investment in mental health care systems is crucial. In many parts of the world, It services are underfunded and understaffed, which results in long wait times and inadequate treatment. Increased funding for mental health care can lead to better access to services and improved outcomes for individuals.
Conclusion
It is an integral part of overall well-being and affects every aspect of our lives. While many mental health challenges are common, they should not be seen as something to hide or be ashamed of. Understanding mental health, reducing stigma, and providing accessible, comprehensive care can help individuals lead healthier, happier lives. Societal efforts to promote mental health awareness, reduce stigma, and invest in resources will create a more compassionate and supportive world for those facing mental health challenges.
By normalizing conversations about mental health and ensuring that mental health care is available to all, we can foster a society where mental well-being is given the attention it deserves and individuals can thrive both personally and professionally.
